The Global Positioning System
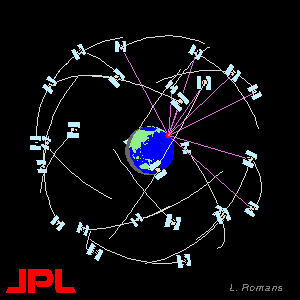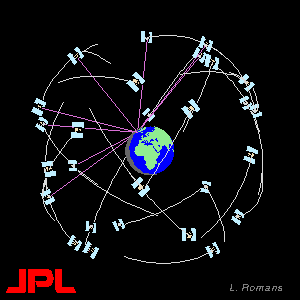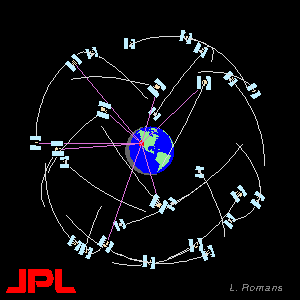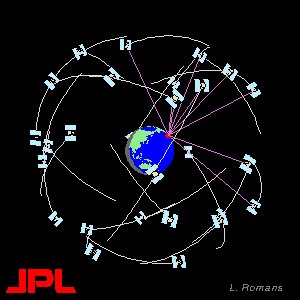
The GPS constellation consists of 24 earth orbiting satellites, in 6 orbital planes. GPS receivers receive signals from the satellites (at least 4 are needed) and use these signals to determine their location. See the References page for more information about the details of how GPS works.

Errors Due to Multipath
One source of error in a GPS position fix is multipath. Multipath is the corruption of a direct GPS signal by one or more signals reflected from surfaces near the receiver (see figure below). Multipath signals can either interfere with or be mistaken for the direct signal. Multipath reflections affect both code and carrier based measurements in a GPS receiver. Code multipath results in the distortion of the signal correlation peak by the presence of the reflected signal. The combination of the direct signal and the delayed signal results in an asymmetric correlation function, resulting in an error in the computed pseudorange to that satellite.
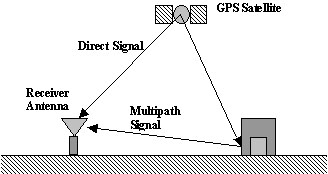
Reflected Signals
In 1960, the first communications satellite was launch, called Echo-1 (shown below). It was a large (100 feet in diameter) aluminized plastic balloon placed in low earth orbit. Radio and TV signals transmitted to the satellite would be reflected back to earth and could be received by any station within view.

The Student Reflected GPS Experiment (SuRGE) is a proposed satellite that would measure GPS signals reflected from the Earth's surface (see picture below). For SuRGE, the multipath signal is actually the measurement, instead of an error source. The SuRGE satellite will have to compute the location on the earth of each reflection from each GPS satellite.

Overview of Project
The purpose of this research project is to investigate the properties of a multipath producing sphere. In this project an aluminum foil covered beach ball will be placed near a GPS antenna, and pseudorange data will be collected. This data will be compared to an data collection without the sphere present, in order to compare the two to determine the effect of the sphere. In addition, a MATLAB simulation will be developed to attempt to simulate the errors due to the presence of the sphere, and the predicted values will be compared to the actual values.